Abstract
Keywords: quality of life, multiple myeloma, ixazomib, thalidomide, dexamethasone
Introduction: Health-related quality of life in patients with multiple myeloma may be affected by the disease itself and by myeloma therapy. Ixazomib is a novel oral proteasome inhibitor with significant activity even in patients with high-risk cytogenetics featuring a favorable toxicity profile. In this phase II study we used ixazomib in combination with thalidomide and dexamethasone (IxaThalDex) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM). Interim treatment results showed an overall response rate of 49.3% in the ITT group, a median PFS of 9.3 months, median overall survival has not been reached yet (EHA 2017, abstract 336). Here, we analyze patient-reported outcomes regarding health-related quality of life in the induction and maintenance phase.
Patients and Methods: At time of analysis, 77 patients with relapsed/refractory MM had been enrolled (median age: 67 years, ISS stage I: 39%, II: 33%, III: 26%, ECOG status 0-1: 95%, 2: 5%). Treatment consisted of 8 cycles of ixazomib, 4mg, d 1, 8 and 15, q 28 days, thalidomide, 100mg/d, and dexamethasone: 40mg d 1, 8, 15. Patients aged ≥75 years had a 50% dose reduction of thalidomide to 50mg/d and of dexamethasone to 20mg. Maintenance treatment consisted of ixazomib, 4mg, days 1, 8, 15 of a 28 day cycle and 3mg in patients aged ≥75 years, and was given for one year.
Health-related quality of life was assessed by the EORTC questionnaires EORTC QOL-C30 and the Myeloma subscale QOL-MY20. Health-related quality of life assessments were done at baseline and before each cycle during induction and maintenance treatment.
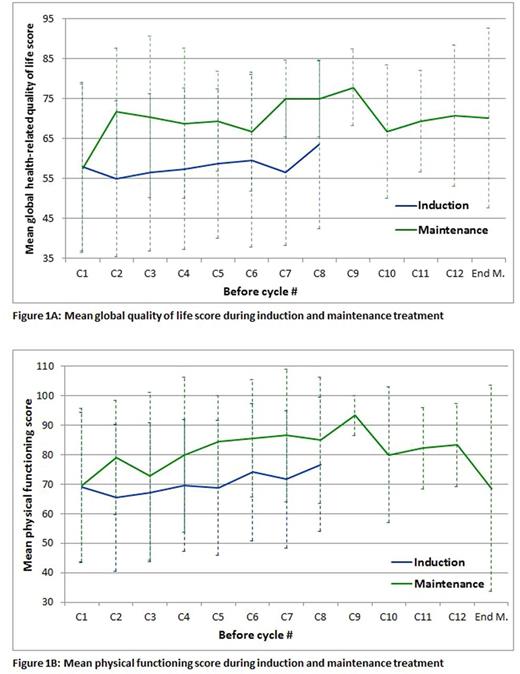
Here, results of global health-related QOL, physical functioning and of 2 symptom subscales that are of major importance for patients, namely pain and fatigue are shown. An increase in score points reflects an improvement for the functional scores global health-related quality of life and physical functioning, while the opposite applies to the symptom scores pain and fatigue.
Results: QOLdata at baseline were available in 77 patients before induction and in 31 patients at start of maintenance therapy. Median follow-up was 11.4 months. Mean global health-related QOL score at baseline (Figure 1A) was 57.9, which is lower than that of a normal population of similar age (65.5, Waldmann A et al., Plos 1, 2013). Among patients staying on protocol therapy, QOL scores remained stable during the entire induction therapy, and were similar at start of maintenance treatment but increased distinctly by more than 10 points after the first months of maintenance and remained stable during the entire maintenance period Figure 1 A. A similar pattern was noted for physical functioning (Figure 1B), with a clinical meaningful improvement (more than 10 points).
Patients presented with significant fatigue (mean score 42.6 versus 29.2 in a normal population of similar age) at start of therapy that remained stable during the 8 cycles of IxaThalDex induction therapy. During maintenance treatment, a tendency towards improvement was noted but this showed substantial variation between cycles probably because of the still limited number of patients who completed the entire maintenance protocol. The mean pain score was 46.1 (versus 31.6 in a normal population of similar age) and improved already during induction therapy. A further relevant improvement was noted during the maintenance phase, which showed a marked improvement which was maintained over the one-year treatment period.
Conclusion: This study is the first to report the impact of Ixazomib maintenance therapy on several dimensions of QOL and provides QOL data during IxaThalDex induction therapy in patients with RRMM. Results show impaired, but stable health-related QOL and physical functioning during IxaThalDex therapy with relevant improvement of health-related QOL and a tendency for better physical functioning during maintenance therapy. Similar findings were obtained for fatigue, while for pain a marked improvement was noted already during the induction phase, which improved further during the maintenance period. Updated results will be presented at the meeting.
Ludwig: Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AMGEN: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen-Cilag: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Meyers: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Knop: Takeda: Consultancy. Hajek: Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharma MAR: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Gunsilius: Takeda, Janssen, Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyers: Honoraria; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Petzer: Takeda, Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Weisel: Sanofi: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Greil: Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel support, Research Funding; Novartis, Celgene: Research Funding; BMS, Amgen: Honoraria. Zojer: Celgene, Janssen, Amgen, Takeda, BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal